Introducing Apache Kafka® 4.0
We are proud to announce the release of Apache Kafka® 4.0. This release contains many new features and improvements. This blog post will highlight some of the more prominent ones. For a full list of changes, be sure to check the release notes.
Apache Kafka 4.0 is a significant milestone, marking the first major release to operate entirely without Apache ZooKeeper™️. By running in KRaft mode by default, Kafka simplifies deployment and management, eliminating the complexity of maintaining a separate ZooKeeper ensemble. This change significantly reduces operational overhead, enhances scalability, and streamlines administrative tasks. We want to take this as an opportunity to express our gratitude to the ZooKeeper community and say thank you! ZooKeeper was the backbone of Kafka for more than 10 years, and it did serve Kafka very well. Kafka would most likely not be what it is today without it. We don’t take this for granted, and highly appreciate all of the hard work the community invested to build ZooKeeper. Thank you!
Kafka 4.0 also brings the general availability of KIP-848, introducing a powerful new consumer group protocol designed to dramatically improve rebalance performance. This optimization significantly reduces downtime and latency, enhancing the reliability and responsiveness of consumer groups, especially in large-scale deployments.
Additionally, we are excited to offer early access to Queues for Kafka (KIP-932), enabling Kafka to support traditional queue semantics directly. This feature extends Kafka’s versatility, making it an ideal messaging platform for a wider range of use cases, particularly those requiring point-to-point messaging patterns.
Kafka's major releases, such as version 4.0, remove APIs deprecated for at least 12 months to simplify the platform, and encourage the adoption of newer features. Notably, in Kafka 4.0, Kafka Clients and Kafka Streams require Java 11, while Kafka Brokers, Connect, and Tools, now require Java 17. This release also updates the minimum supported client and broker versions (KIP-896), and defines new baseline requirements for supported upgrade paths. Further details are provided in subsequent sections of this document.
These highlights illustrate Kafka's continued evolution to meet the demands of modern, scalable, and efficient data streaming and messaging architectures.
See the Upgrading to 4.0 section in the documentation for the list of notable changes and detailed upgrade steps.
Kafka Broker, Controller, Producer, Consumer and Admin Client
KIP-848: The Next Generation of the Consumer Rebalance Protocol
Apache Kafka says goodbye to “stop-the-world” rebalances with the general availability of the next generation of the consumer rebalance protocol. It increases the stability and the performance of consumer groups while simplifying clients. The new protocol is enabled by default on the server side. Consumers must opt-in by setting
group.protocol=consumer. See here for details.KIP-890: Transactions Server-Side Defense
The second phase of KIP-890 has been completed. It reduces the chances of “zombie transactions” during producer failures. See here for details.
KIP-932: Queues for Kafka (Early Access)
This KIP introduces the concept of a share group as a way of enabling cooperative consumption using Kafka topics. It does not add the concept of a “queue” to Kafka per se, but rather introduces cooperative consumption to accommodate these queuing use-cases, using regular Kafka topics. Share groups make this possible. You can think of a share group as roughly equivalent to a “durable shared subscription” in existing systems. Please see the Early Access Release Notes for limitations and configurations.
KIP-966: Eligible Leader Replicas (Preview)
KIP-966 introduces Eligible Leader Replicas (ELR) in preview in 4.0. ELR is a subset of the ISR replicas guaranteed to have complete data up to the high-watermark. ELRs are safe for leader election, preventing data loss. See here for details.
KIP-996 introduces a "Pre-Vote" mechanism to reduce unnecessary KRaft leader elections in Apache Kafka clusters. By allowing nodes to check their eligibility for leadership before initiating an election, this approach minimizes disruptions caused by network partitions or transient issues.
KIP-1076: Metrics for client applications KIP-714 extension
With KIP-714, cluster operators can now collect client metrics directly from brokers using a plugin. This makes it much easier to monitor client behavior. However, KIP-714 only gathers metrics from Kafka clients (admin, consumer, and producer), and doesn't cover application-level metrics for embedded clients, such as Kafka Streams. To fully understand performance, it's important to collect both client metrics and application-specific metrics. This KIP introduces a way for applications that use Kafka clients to include their own metrics alongside the existing client metrics.
KIP-1106: Add duration based offset reset option for consumer clients
Kafka consumers support the
auto.offset.resetconfig option, which is used when there is no initial offset in Kafka, or if the current offset does not exist any more on the server. This config currently supports earliest/latest/none options. Currently consumer resets might force applications to reprocess large amounts of data from earlier offsets. With infinite storage, it's beneficial to have a duration based offset reset strategy. This KIP allows applications to consume/initialize from a fixed duration when there is no initial offset in Kafka.KIP-1043: Administration of groups
KIP-848 and KIP-932 introduce new group types, consumer and share, respectively. The Admin Client API has limitations when dealing with newer group types, sometimes returning errors or incorrectly stating that groups don't exist. To address this challenge, a new command-line tool,
kafka-groups.sh, and updates to existing command line tools,kafka-consumer-groups.shandkafka-share-groups.sh, were made in Kafka 4.0 to enable users to view all groups in a cluster, along with their types and protocols—providing accurate information even when the Admin Client API fails.KIP-1099: Extend kafka-consumer-groups command line tool to support new consumer group
This KIP extends the
kafka-consumer-groups.shand thekafka-share-groups.shcommand line tools to provide more information related to consumer and share groups. This helps when it comes to troubleshooting consumer and share groups, respectively introduced by KIP-848 and KIP-932.KIP-1102: Enable clients to rebootstrap based on timeout or error code KIP-1102 enhances Kafka client resilience by proactively triggering metadata rebootstrap when no updates occur within a timeout period, and allowing servers to explicitly signal clients to rebootstrap. This addresses previous limitations in KIP-899, where clients could become stuck with outdated metadata unless all brokers were unreachable.
KIP-896: Remove old client protocol API versions in Kafka 4.0
For the first time, old protocol API versions have been removed. Users should ensure brokers are version 2.1 or higher before upgrading Java clients (including Connect and Streams) to 4.0. Similarly, users should ensure their Java client version is 2.1 or higher before upgrading brokers to 4.0.
KIP-1124: Providing a clear Kafka Client upgrade path for 4.x
This KIP outlines the upgrade path for Kafka Clients, Streams and Connect to 4.0. It is a must read before upgrading your clusters and clients.
KIP-653: Upgrade log4j to log4j2
The logging framework has been migrated from Log4j to Log4j2. Users can use the log4j-transform-cli tool to automatically convert their existing Log4j configuration files to Log4j2 format. Users can also keep using their Log4j configurations, but with certain limitations. Check the migration guide for details.
KIP-724: Drop support for message formats v0 and v1
The message formats v0 and v1 were deprecated in Apache Kafka 3.0. They have been removed in 4.0.
KIP-750: Drop support for Java 8 in Kafka 4.0 (deprecate in 3.0) and KIP-1013: Drop broker and tools support for Java 11 in Kafka 4.0 (deprecate in 3.7)
Kafka Clients and Kafka Streams require Java 11, while Kafka Brokers, Connect and Tools now require Java 17.
KIP-1030: Change constraints and default values for various configurations
KIP-1030 has changed the default values of some configurations in order to provide better defaults to users starting out using Apache Kafka. Check out the KIP for the details.
Kafka Streams
KIP-1104: Allow Foreign Key Extraction from Both Key and Value in KTable Joins
KIP-1104 enhances Kafka Streams by allowing foreign keys to be extracted directly from both record keys and values, removing the need to duplicate keys into values for foreign-key joins. This improvement simplifies joins, reduces storage overhead, and provides a more intuitive developer experience.
KIP-1112: Allow custom processor wrapping
KIP-1112 simplifies applying cross-cutting logic in Kafka Streams by introducing the
ProcessorWrapperinterface, enabling seamless injection of custom logic around Processor API and DSL processors. This eliminates previous redundancy and reduces the maintenance overhead caused by manually integrating logic into each processor individually.KIP-1065: Add "retry" return-option to ProductionExceptionHandler
KIP-1065 addresses persistent errors in Kafka Streams by allowing users to break retry loops via a new "RETRY" option in the
ProductionExceptionHandler. This enhancement provides customizable error handling, enabling retries, graceful failures, or dropping problematic records to continue processing efficiently.KIP-1091: Improved Kafka Streams operator metrics
Kafka Streams exposes its metrics with KIP-1076. This KIP specifically adds a state metric for each StreamThread and the client instance itself. It also provides detailed visibility into application state.
Kafka Connect
KIP-970: Deprecate and remove Connect's redundant task configurations endpoint
The endpoint
GET /connectors/{connector}/tasks-configadded in KIP-661 was deprecated in Apache Kafka 3.7 and is finally removed in 4.0. The endpointGET /connectors/{connector}/tasksmust be used as a replacement.KIP-1074: Allow the replication of user internal topics
Previously, MirrorMaker 2 automatically excluded topics whose names ended with .internal or -internal, incorrectly classifying them as internal topics. This behavior prevented legitimate business topics from being replicated unless users implemented a custom replication policy. This KIP introduces a configurable option that allows users to replicate such topics without requiring custom code.
KIP-1089: Allow disabling heartbeats replication in MirrorSourceConnector
Previously, MirrorSourceConnector always replicated heartbeat topics, which could cause issues when multiple connectors with different configurations replicated topics between the same clusters, resulting in duplicate heartbeat replication. This KIP introduces a configurable option to disable heartbeat topic replication, providing users greater flexibility, particularly when using multiple connectors with distinct configurations.
KIP-1032: Upgrade to Jakarta and JavaEE 10 in Kafka 4.0
Kafka Connect previously utilized outdated JavaEE APIs, restricting its compatibility with contemporary Jakarta EE frameworks and applications. KIP-1032 addresses this by upgrading Kafka 4.0 to Jakarta EE and JavaEE 10 APIs, introducing Java 17 as a required minimum version, and aligning Kafka with current standards for improved maintainability.
Summary
Ready to get started with Apache Kafka 4.0.0? Check out all the details in the upgrade notes and the release notes, and download Apache Kafka 4.0.0.
This was a community effort, so thank you to everyone who contributed to this release, including all our users and our 175 contributors:
A. Sophie Blee-Goldman, abhi-ksolves, Abhijeet Kumar, Abhinav Dixit, Abhishek Giri, Alieh Saeedi, Almog Gavra, Alyssa Huang, Andrew Schofield, Anshul Goyal, Ao Li, Apoorv Mittal, Arnav Dadarya, Arpit Goyal, Artem Livshits, Ayoub Omari, bachmanity1, bboyleonp666, Bill Bejeck, brenden20, Bruno Cadonna, Caio Guedes, Calvin Liu, Chengyan, Cheryl Simmons, Chia-Chuan Yu, Chia-Ping Tsai, Chirag Wadhwa, Chris Egerton, Christo Lolov, Christopher L. Shannon, ClarkChen, Clay Johnson, Colin P. McCabe, Colt McNealy, Danica Fine, Dániel Urbán, David Arthur, David Jacot, David Mao, David Schlosnagle, Dejan Stojadinović, devanshikhatsuriya, Dimitar Dimitrov, Divij Vaidya, DL1231, Dmitry Werner, donaldzhu-cc, Dongnuo Lyu, dujian0068, Edoardo Comar, Eric Chang, Federico Valeri, Frederik Rouleau, GangHuo, Gantigmaa Selenge, Gaurav Narula, Greg Harris, Guozhang Wang, Hailey Ni, Hongten, Hyunsang Han, Ian McDonald, Igor Soarez, Ismael Juma, Ivan Yurchenko, Jakub Scholz, Jason Gustafson, Jason Taylor, Jeff Kim, Jhen-Yung Hsu, Jim Galasyn, João Pedro Fonseca Dantas, John Huang, JohnHuang, Jonah Hooper, José Armando García Sancio, Josep Prat, Jun Rao, Justin Lee, Justine Olshan, Kamal Chandraprakash, KApolinario1120, kartik-3513, Kaushik Raina, Ken Huang, kevin-wu24, Kirk True, Kondrat Bertalan, Krishna Agarwal, Kuan-Po Tseng, kwonyonghyun, Laxman Ch, Liam Miller-Cushon, Lianet Magrans, Linsiyuan9, Linu Shibu, Liu Zeyu, Logan Zhu, Loïc Greffier, Lucas Brutschy, Luke Chen, lushilin, Mahsa Seifikar, Manikumar Reddy, mannoopj, Martin Sillence, Mason Chen, Matthias J. Sax, Mehari Beyene, Mickael Maison, Ming-Yen Chung, mingdaoy, msureshpro, Murali Basani, Nancy, Nick Guo, Nick Telford, Oleg Bonar, Oleksandr K., Omnia Ibrahim, Parker Chang, Patrik Marton, Paul R. Mellor, Peter Lee, Philip Nee, PoAn Yang, Rajini Sivaram, Ramin Gharib, Ritika Reddy, Robert Young, Rohan, S.Y. Wang, Said Boudjelda, Sanskar Jhajharia, santhoshct, Sasaki Toru, Satish Duggana, Saxon Chen, Scott Hendricks, Sean Quah, Sebastien Viale, Shivsundar R, snehashisp, Stanislav Knot, Steven Xu, stevenbooke, Stig Døssing, Sushant Mahajan, Swikar Patel, TaiJuWu, tall15421542-lab, TapDang, Ted Yan, TengYao Chi, Thomas Thornton, Tim Fox, tkuramoto33, Tom Duckering, Vedarth Sharma, Vikas Singh, Viktor Somogyi-Vass, Vincent Jiang, wperlichek, xijiu, Xuan-Zhang Gong, yangjf2019, Yaroslav Kutsela, Yash Mayya, Yung, yungh, yx9o, Zhengke Zhou, Ziming Deng, 陳昱霖 (Yu-Lin Chen)
This blog post was originally published by David Jacot on The Apache Software Foundation blog.
Apache®, Apache Kafka®, Kafka®, and Apache ZooKeeper™️ are either registered trademarks or trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation in the United States and/or other countries. No endorsement by the Apache Software Foundation is implied by using these marks. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
このブログ記事は気に入りましたか?今すぐ共有
Confluent ブログの登録
How To Delete a Topic in Apache Kafka®: A Step-By-Step Guide
Learn how to delete topics in Apache Kafka safely and efficiently. Explore step-by-step instructions, best practices, and important considerations for managing Kafka topics.
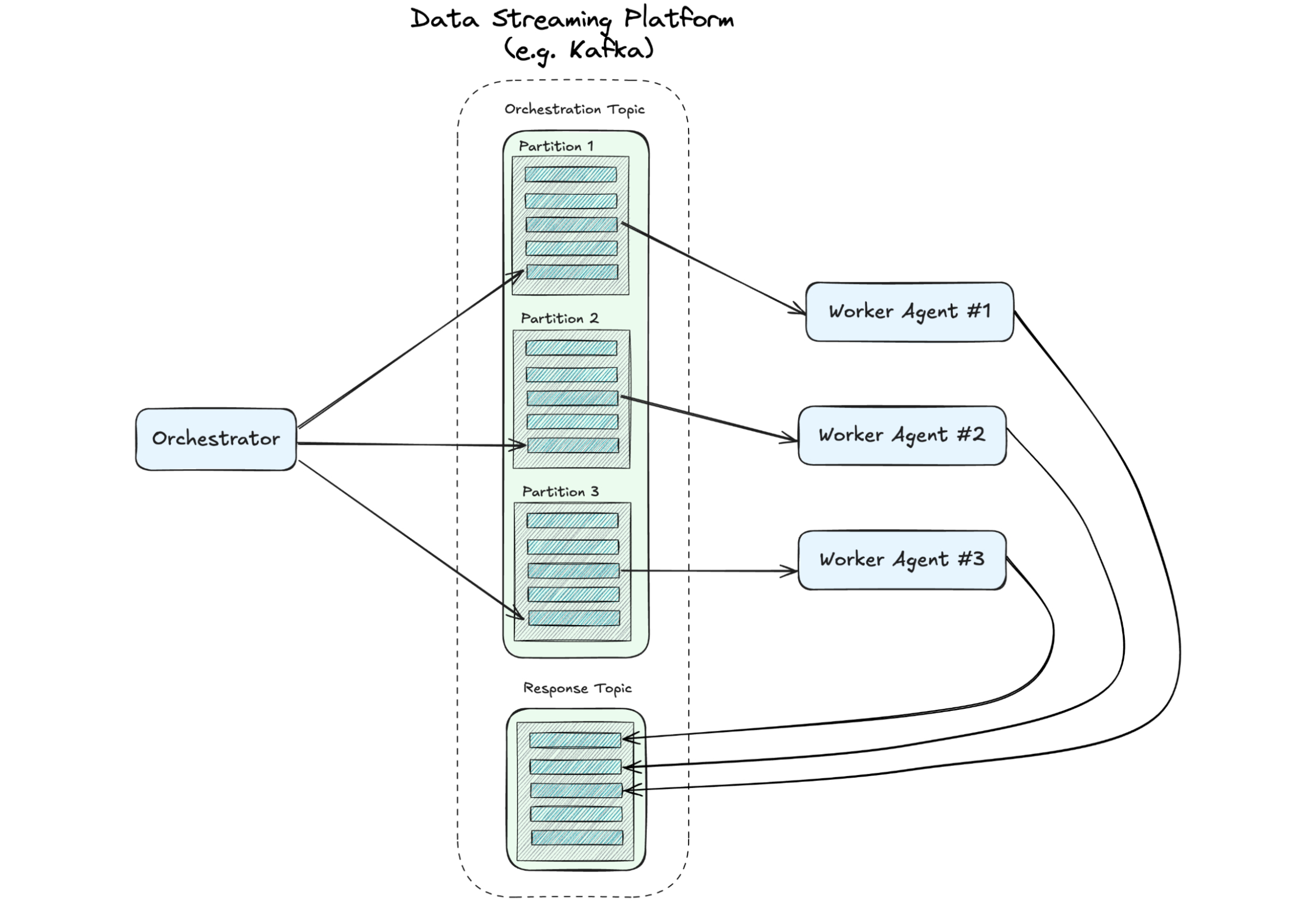
A Distributed State of Mind: Event-Driven Multi-Agent Systems
This article explores how event-driven design—a proven approach in microservices—can address the chaos, creating scalable, efficient multi-agent systems. If you’re leading teams toward the future of AI, understanding these patterns is critical. We’ll demonstrate how they can be implemented.